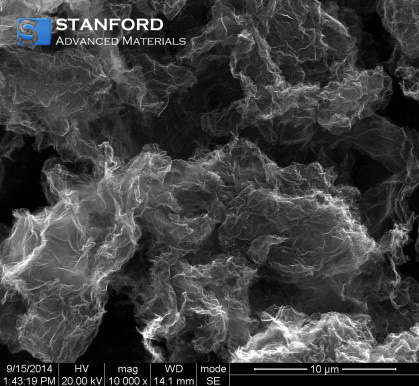
Nitrogen Doped Graphene Description
Graphene is a new material with a monoatomic layer sheet structure composed of carbon atoms. It has excellent light transmittance and thermal conductivity. It is the thinnest, hardest, and least resistive material known.
Nitrogen-doped graphene (N-graphene) is obtained by exposing graphene to nitrogen plasma. N-graphene exhibits much higher electrocatalytic activity toward oxygen reduction and H2O2 reduction than graphene, and much higher durability and selectivity than the widely-used expensive Pt for oxygen reduction. The excellent electrochemical performance of N-graphene is attributed to nitrogen functional groups and the specific properties of graphene.
Nitrogen Doped Graphene Specifications
|
Purity
|
>98%
|
|
Thickness (nm)
|
1-3
|
|
Size (μm)
|
2-10
|
|
Form
|
Black powder
|
|
Nitrogen Content %
|
5-10
|
|
Number of layers
|
<3
|
|
Specific Surface Area (m2/g)
|
100-300
|
|
Tap Density (mg/mL)
|
5-10
|
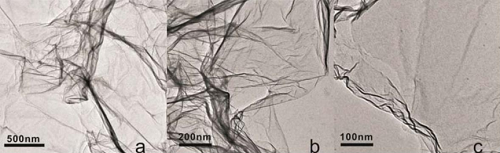
Nitrogen Doped Graphene TEM
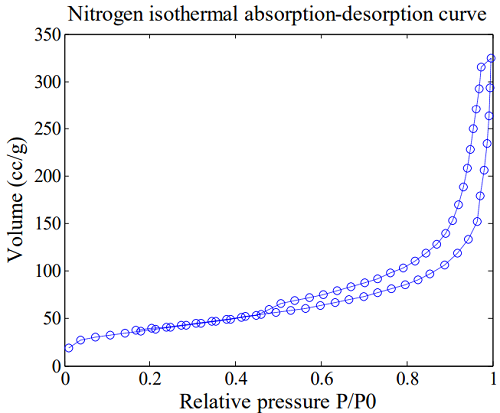
Nitrogen Doped Graphene Absorption-desorption Curve
Nitrogen Doped Graphene Applications
1. Electrocatalysis: Nitrogen doping enhances graphene’s catalytic activity, making it a promising alternative to precious metal catalysts (like platinum) in fuel cells, metal-air batteries, and other energy conversion applications.
2. Energy Storage: NDG is used in lithium-ion, sodium-ion, and supercapacitor electrodes. The nitrogen atoms improve the material’s conductivity and energy storage capacity, contributing to faster charge/discharge rates and higher energy densities.
3. Sensors: Nitrogen-doped graphene is highly sensitive to various molecules, making it useful in gas and biosensors for detecting environmental pollutants, gases, or biological markers in medical diagnostics.
4. Photocatalysis: NDG has shown promise in photocatalytic applications, such as water splitting and CO₂ reduction, due to its enhanced light absorption and electron transfer properties, driven by nitrogen doping.
5. Biomedical Applications: In drug delivery and bioimaging, NDG's biocompatibility and surface functionality allow it to interact with biomolecules, making it useful for targeted drug delivery and biosensing applications.
6. Supercapacitors: NDG is used to create electrodes with higher surface area and conductivity for supercapacitors, enhancing energy storage capabilities and performance in power electronics.
7. Anti-Corrosion Coatings: The material can be applied as a coating to protect metals and other materials from corrosion, utilizing its chemical stability and protective surface properties.
8. Water Purification: Due to its enhanced adsorption properties, NDG can be used to remove heavy metals, organic pollutants, and other contaminants from water in filtration systems.
9. Solar Cells: NDG’s improved charge transfer and light absorption make it valuable in dye-sensitized and other types of solar cells, potentially boosting efficiency and stability.
Nitrogen Doped Graphene Packaging
Our Nitrogen Doped Graphene is carefully handled during storage and transportation to preserve the quality of our product in its original condition.