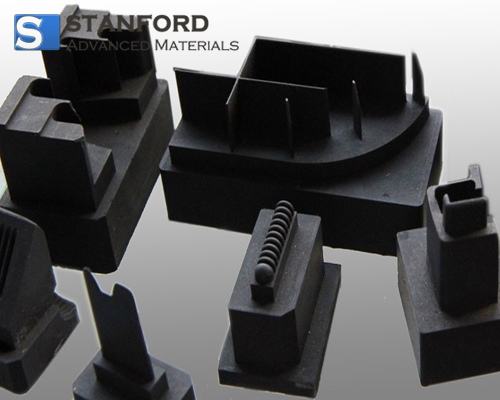
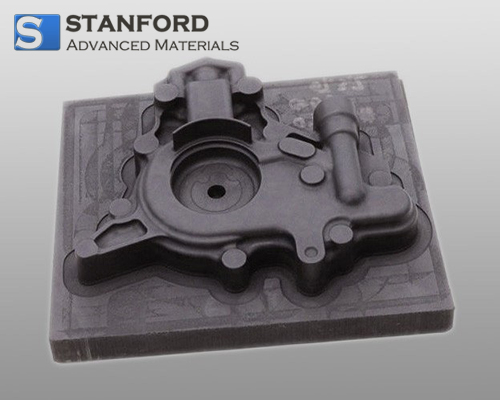
Molded Graphite Description
Molded Graphite is a specialized form of graphite produced by compressing graphite powder into specific shapes and then heat treating it to enhance its properties. This material exhibits several key characteristics, including high strength and rigidity, which make it suitable for structural applications requiring durability. It has superior thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat transfer, and good electrical conductivity, making it useful in applications such as electrodes for batteries and electric arc furnaces. Additionally, Molded Graphite has a low coefficient of thermal expansion, ensuring dimensional stability under varying temperatures, and is resistant to many chemicals, including acids and alkalis, which makes it ideal for use in corrosive environments. Its self-lubricating properties reduce friction in mechanical applications, while its lightweight nature offers advantages in weight-sensitive applications. These combined properties make Molded Graphite an excellent choice for a wide range of industrial applications, including electronics, automotive, aerospace, and metal processing.
Molded Graphite Specifications
|
Grade
|
MG 1
|
MG 2
|
|
Density g/cc
|
1.85
|
1.78
|
|
Grain Size
|
43 micro
|
43 micro
|
|
Resistance μΩ·m
|
9
|
9.1
|
|
Compressive Strength MPa
|
81
|
71
|
|
Flexural Strength MPa
|
40
|
36
|
|
Shore Hardness
|
41
|
35
|
|
Thermal Expansion (CTE)
(20-100℃) 10-6/℃
|
4.4
|
4.7
|
|
Thermal Conductivity (100℃)
W/mk
|
140
|
120
|
|
Porosity %
|
13
|
17
|
Molded Graphite Applications
1. Electrodes: Used in electric arc furnaces and in the production of batteries, where high electrical conductivity is essential.
2. Sealing Materials: Employed in gaskets and seals for high-temperature and corrosive environments due to its chemical resistance and durability.
3. Heat Exchangers: Utilized in heat transfer applications, including heat exchangers and cooling systems, due to its excellent thermal conductivity.
4. Aerospace Components: Used in the aerospace industry for lightweight structural components that require high strength and stability at elevated temperatures.
5. Automotive Parts: Applied in manufacturing parts such as brake linings, bushings, and other components that benefit from its self-lubricating properties.
6. Metal Casting: Used as molds and die materials in foundries due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and maintain shape under thermal stress.
7. Nuclear Applications: Employed in nuclear reactors as a moderator and in other applications where high thermal resistance is required.
8. Consumer Electronics: Used in components like heat sinks and conductive parts for improved thermal management and electrical performance.
9. Pumping Equipment: Utilized in the manufacture of pump components where resistance to wear and corrosion is important.
Molded Graphite Packaging
Our Molded Graphite is carefully handled during storage and transportation to preserve the quality of our product in its original condition.