Sodium Hyaluronate Products of Different Technical Specifications: Molecular Weight and Viscosity
Introduction
Sodium hyaluronate (SH), the salt form of hyaluronic acid, is a naturally occurring polysaccharide. It has become increasingly popular in the cosmetic and medical industries for its ability to improve skin hydration, texture, and overall appearance. SH is available in a range of technical specifications, including different molecular weights and viscosities, which can impact its performance in diverse applications. In this article, we will explore the different types of SH products and their matched applications. Hope that you can have a better comprehension and select the perfect sodium hyaluronate products for your business and research.
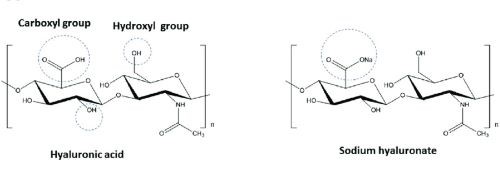
Figure 1. Chemical Structure of HA And SH
Sodium Hyaluronate: Molecular Weight
The molecular weight of SH is a critical factor that determines its physical and biological properties. In general, the higher the molecular weight of SH, the greater its viscosity and elasticity. Thus, higher molecular weight HA is ideal for use in cosmetic applications; on the other hand, lower molecular weight SH is typically used in medical applications, where it can be more easily absorbed by the body.
- Low Molecular Weight SH (LMW-SH): LMW-SH has a molecular weight of fewer than 1000 kDa and is commonly used in medical applications, such as joint injections for osteoarthritis. LMW-SH is highly bioavailable and can be rapidly absorbed by the body, rendering it effective for reducing inflammation and improving joint function.
- Medium Molecular Weight SH (MMW-SH): MMW-SH has a molecular weight of 1000-1500 kDa and is widely employed in cosmetic applications, such as dermal fillers and skin moisturizers. MMW-SH has a moderate viscosity and elasticity, making it effective for filling in wrinkles and adding volume to the skin.
- High Molecular Weight SH (HMW-SH): HMW-SH has a molecular weight of more than 1500 kDa and is also applied to cosmetic fields. HMW-SH has a high viscosity and elasticity, which is useful for long-lasting volume restoration and hydration of the skin.
Related reading: High VS. Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid
Sodium Hyaluronate: Viscosity
The viscosity of SH is another important factor that determines its suitability for different applications. High-viscosity SH is typically used in cosmetic applications, where it can provide a thick, gel-like texture that fills in wrinkles and adds volume to the skin. Low-viscosity SH is extensively utilized in medical applications, where it can be easily injected into the body.
- Low Viscosity SH: Low viscosity SH has a viscosity of less than 50,000 mPa·s and is commonly used to make joint injections and other medical devices. It is highly bioavailable and can be rapidly absorbed by the body, thus reducing inflammation and improving joint function.
- Medium Viscosity SH: Medium viscosity SH has a viscosity of 50,000-1,000,000 mPa·s and is typically applied to manufacture dermal fillers, skin moisturizers, and other cosmetic products. It has a moderate texture, which could fill in wrinkles and add volume to the skin.
- High Viscosity SH: High viscosity SH has a viscosity of more than 1,000,000 mPa·s, and it finds applications in cosmetic sectors. It has a thick, gel-like texture, which is beneficial to long-lasting volume restoration and hydration of the skin.
Related reading: Viscosity, Molecular Weight and Rheological Properties of HA
Conclusion
In a word, sodium hyaluronate products are available in a range of technical specifications, including different molecular weights and viscosities, which can impact their performance in diverse applications. Understanding the matched application of SH products is crucial for achieving the desired results and ensuring safe and effective use. By selecting the appropriate SH product based on the specific application, healthcare providers and consumers can benefit from the many advantages of this versatile and effective polysaccharide.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a trustful supplier of sodium hyaluronate of various specifications. We have high molecular weight, middle molecular weight, and low molecular weight sodium hyaluronates. Customization is welcome as well. Please check our website for more details.
Reference:
[1] Khaleghi, Maryam & Ahmadi, Ebrahim & Shahraki, Mahvash & Aliakbari, Farhang & Morshedi, Dina. (2020). Temperature-dependent formulation of a hydrogel based on Hyaluronic acid-polydimethylsiloxane for biomedical applications. Heliyon. 6. e03494. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03494.