Density: Measurement and Common Materials
What Is Density
Density is a fundamental property of matter that describes how much mass is contained in a given volume. It is a crucial parameter in various scientific and engineering applications, influencing material selection and behavior under different conditions.
Measurement of Density
Measuring density accurately is essential in both laboratory and industrial settings. Several methods are commonly used:
Mass and Volume Method
The simplest way to determine density is by measuring an object's mass and volume, and then applying the formula:
Density=Mass/Volume
Archimedes' Principle
This principle involves submerging an object in a fluid to determine its volume based on the displacement of the fluid, which can then be used to calculate density.
Pycnometer Method
A pycnometer is a specialized container used to measure the density of liquids and solids with high precision by determining their volume through displacement.
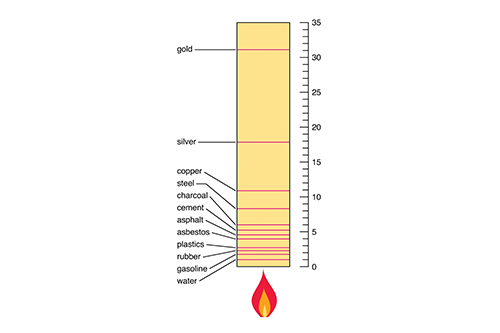
Density of Common Materials
Here’s a table summarizing the density of common materials. Density is the mass per unit volume, usually measured in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³).
|
Material |
Density (g/cm³) |
Density (kg/m³) |
Notes |
|
2.70 |
2700 |
Lightweight, commonly used in aerospace and automotive. |
|
|
Copper |
8.96 |
8960 |
Heavy metal with high electrical conductivity. |
|
Steel (Carbon Steel) |
7.85 |
7850 |
Common structural material, strong and durable. |
|
Cast Iron |
6.90 |
6900 |
Used in heavy-duty applications like engine blocks. |
|
4.43 |
4430 |
Strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant. |
|
|
Stainless Steel (304) |
7.93 |
7930 |
Corrosion-resistant, used in food processing and marine environments. |
|
Brass |
8.50 |
8500 |
Alloy of copper and zinc, used in plumbing and electrical applications. |
|
Lead |
11.34 |
11340 |
Very dense, used in radiation shielding and batteries. |
|
19.25 |
19250 |
Extremely dense, used in high-temperature and radiation shielding applications. |
|
|
Nickel |
8.90 |
8900 |
Often used in alloys and as a coating for corrosion resistance. |
|
Gold |
19.32 |
19320 |
Dense, highly valued precious metal. |
|
Silver |
10.49 |
10490 |
Valuable metal used in jewelry and electronics. |
|
Wood (Oak) |
0.75-0.85 |
750-850 |
Density varies depending on wood type and moisture content. |
|
Concrete |
2.30 |
2300 |
Density depends on the mix; used in construction. |
|
Glass |
2.40-2.80 |
2400-2800 |
Used in windows, containers, and electronics. |
|
Polyethylene (Plastic) |
0.91-0.96 |
910-960 |
Lightweight plastic commonly used for packaging. |
|
Wood (Pine) |
0.50-0.65 |
500-650 |
Lighter than oak, used for furniture and construction. |
|
Carbon Fiber |
1.60-2.00 |
1600-2000 |
Lightweight, high-strength composite material. |
|
Glass Fiber |
2.50-2.70 |
2500-2700 |
Strong composite material used in aerospace and marine. |
|
Rubber |
1.10-1.60 |
1100-1600 |
Used in tires, seals, and flexible components. |
|
Silicon |
2.33 |
2330 |
Common in electronics and solar cells. |
|
1.85 |
1850 |
Lightweight, high-strength material used in aerospace and nuclear applications. |
Notes: Higher density materials (e.g., tungsten, lead) are typically used in applications requiring mass or stability, while lower density materials (e.g., aluminum, plastics) are preferred where weight reduction is important. For more advanced materials, please check Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM).
Applications of Density
Density plays a critical role in numerous fields:
- Engineering: Selecting materials with appropriate densities for structural components.
- Geology: Identifying minerals and understanding geological formations.
- Manufacturing: Ensuring material consistency and quality control.
- Environmental Science: Assessing pollutant distribution in air and water.
Factors Affecting Density
Several factors can influence the density of a material:
- Temperature: Generally, as temperature increases, density decreases due to expansion.
- Pressure: Increased pressure can compress materials, increasing their density.
- Composition: The elemental makeup and molecular structure determine intrinsic density.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the formula for calculating density?
Density is calculated by dividing an object's mass by its volume (Density = Mass/Volume).
Why is density important in material selection?
Density helps determine the suitability of a material for specific applications based on weight and strength requirements.
How does temperature affect the density of liquids?
As temperature increases, liquids typically expand, resulting in a decrease in density.
Can density be used to identify substances?
Yes, density is a unique property that can help identify and differentiate substances.
What is the difference between mass and density?
Mass is the amount of matter in an object, while density is the mass per unit volume of that object.