Application of Titanium in the Automotive Industry
Titanium is a silvery-white transition metal, which is characterized by lightweight, high strength, metallic luster, and resistance to wet chlorine corrosion. In this article, let's take a closer look at the application of titanium in the automotive industry. Now with the advent of advanced technology automotive industries are using titanium, predominantly in motorcycle racing.

Application of Titanium in the Automotive Industry
The Background
The main focus here is the aspects like weight reduction, improved and rapid performance. No doubt, the vehicles made with titanium applications are verified to be environmentally friendly and fuel-efficient, while the main drawback of the metal is that it is too costly to put together as marketable in the general consumer market.
The recent automotive designers need to engineer the motor vehicles and the parts with less weight using titanium tubes and titanium welded tubes while enabling private cars in particular to give the perfect look and style.
Making cars smaller and trendy is the fashion nowadays. Thus the strategy obviously finds an issue with the management of free space inside the vehicles. The designers here have to adjust the space for the passengers and their effects. Everybody needs lighter cars with no compromise with class and space. Apart from that, the designer has to comply with the reduction of fuel consumption, as well as the environment green image of the production process. Only the material titanium can fulfill all the criteria and conditions. Though it is a little bit expensive, titanium alloys are the best and widely used in the racing car industry.
The quality of metal used and the manufacturing time of soaring performance products in the segment of motor vehicles and automobiles are the key factors. High-strength titanium material is required to manufacture the engine parts of the racing cars as it needs to deliver high output, fast rotation, and high response. The automotive industry made great progress using the metal titanium. The advanced titanium mechanism improves the corrosion resistance of the vehicles, manages the space, and reduces the weight, which results in more fuel savings.
The beneficial properties such as lightweight, corrosive resistance, and high strength of the silvery metal would make it an appealing alternative for various automotive applications. Just the cost of the expensive material stands as a great barrier in the way of its wide usability. That is the reason why it is not found in abundance as in the industries like aerospace.
But now with the advent of some new techniques, the manufacturers are engaged in discovering innovative ways to produce low-cost titanium which can be easily affordable in the different areas of application. So as the costs prolong to decline, the prospective for consumer-based applications will go on with making the use of titanium a more significant alternative.
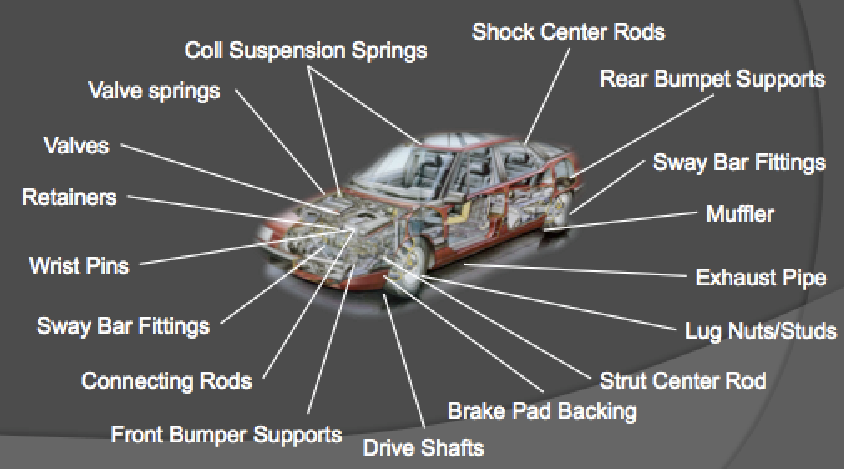
Key Applications of Titanium in Automobiles
1. Exhaust Systems
Titanium is widely used in high-performance exhaust systems due to its heat resistance, durability, and weight reduction benefits. Many sports and luxury cars incorporate titanium exhausts to enhance engine efficiency and reduce emissions.
2. Engine Components
- Valves and Valve Springs: Titanium valves are lighter than traditional steel valves, reducing inertia and improving engine response and efficiency.
- Connecting Rods: Used in high-performance engines to enhance durability and reduce weight, contributing to better acceleration and power output.
3. Suspension Systems
Titanium alloys are used in suspension springs and fasteners, leading to weight savings while maintaining strength and flexibility. This improves handling and ride comfort in performance vehicles.
4. Chassis and Structural Components
Some high-end and racing vehicles incorporate titanium in chassis components to optimize weight distribution and enhance crash resistance without compromising strength.
5. Fasteners and Bolts
Titanium fasteners are used in critical areas of vehicles where strength, lightweight properties, and corrosion resistance are required. They are commonly found in racing and aerospace-inspired road cars.
Advantages of Titanium in Automotive Applications
The use of titanium in vehicles offers numerous benefits:
- Lightweight: Titanium is approximately 45% lighter than steel while maintaining comparable strength, reducing overall vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Provides superior structural integrity without adding excessive weight.
- Corrosion Resistance: Titanium naturally forms a protective oxide layer, making it highly resistant to rust and environmental degradation.
- Heat and Wear Resistance: Excellent performance in high-temperature environments, making it ideal for engine components and exhaust systems.
- Sustainability: Titanium is recyclable, aligning with the automotive industry's push for eco-friendly manufacturing and reduced carbon emissions.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading our article and we hope it can help you to have a better understanding of the application of titanium in the automotive industry. If you want to learn more about titanium and titanium alloys, we would like to advise you to visit Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) for more information.