Top 6 Medical Applications of Nitinol
Introduction
The evolution of medical technology has significantly improved patient outcomes, and one of the most transformative materials in modern healthcare is Nitinol. This article is going to cover the top six medical applications of Nitinol, highlighting its advantages and real-world case studies that demonstrate its effectiveness.
What’s Nitinol Wire?
Nitinol is a nickel-titanium alloy known for its unique properties of superelasticity and shape memory. Superelasticity allows Nitinol to return to its original shape after being deformed, while its shape memory property enables it to revert to a predetermined shape upon heating. These features, combined with biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, have made Nitinol indispensable in modern medical devices.
Benefits of Nitinol Medical Devices
Nitinol-based medical devices offer several advantages over traditional materials. These include:
- Superelasticity: Provides flexibility and resilience, reducing the risk of damage during procedures.
- Shape Memory: Ensures precise deployment in minimally invasive surgeries.
- Biocompatibility: Reduces the likelihood of adverse reactions within the body.
- Corrosion Resistance: Enhances durability and longevity within biological environments.
- Fatigue Resistance: Maintains structural integrity over repeated cycles of use.
- Minimally Invasive Applications: Enables smaller incisions, reducing recovery time and complications.
Top Medical Applications of Nitinol
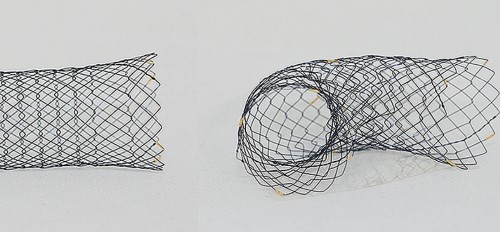
1. Stents
Nitinol stents are widely used in cardiovascular and peripheral vascular interventions. Their superelastic properties allow them to be compressed for catheter-based delivery and expanded to their original shape once deployed in the blood vessel. This ability helps maintain proper blood flow by keeping arteries open.
A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that patients receiving Nitinol self-expanding stents for femoropopliteal artery disease had a primary patency rate of 83.2% at 12 months, compared to 64.8% for balloon-expandable stents, highlighting the superior performance of Nitinol-based devices.[1]
 [2]
[2]
Fig. 1 Self-expanding Stents
2. Guidewires
Nitinol guidewires provide flexibility, kink resistance, and excellent maneuverability during minimally invasive procedures. These wires are used to navigate through complex vascular pathways, enabling the placement of catheters and other interventional devices. Their high elasticity reduces the risk of vessel damage, making them essential in procedures such as angioplasty and endovascular surgeries.
Research has shown that Nitinol guidewires reduce procedural complications by 25% compared to stainless steel alternatives due to their superior torque control and flexibility, making them a preferred choice in coronary interventions.
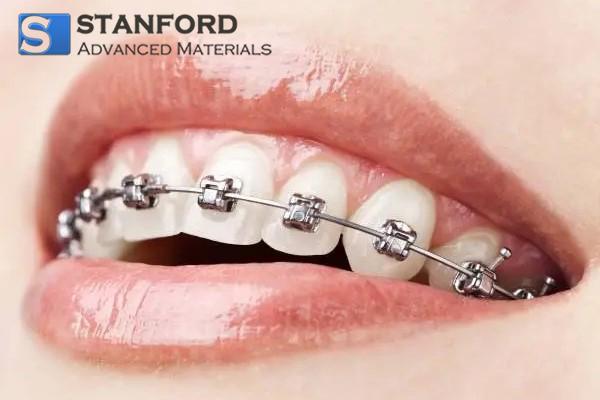
3. Orthodontic Archwires
In orthodontics, Nitinol archwires are a preferred choice due to their shape memory and superelasticity. These wires exert continuous, gentle pressure on teeth, promoting efficient and less painful realignment. Unlike stainless steel wires, Nitinol wires maintain their force over time, reducing the frequency of adjustments and improving patient comfort throughout the treatment process.
A clinical trial in the American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics reported that patients using Nitinol archwires experienced 30% faster alignment in the first 6 months compared to those using conventional stainless steel wires, demonstrating their efficiency.[3]

Fig. 2 Orthodontic Archwires
4. Endovascular Clot Retrieval Devices
Nitinol is a crucial material in clot retrieval devices used for stroke treatment. These devices, often in the form of stent retrievers, are designed to restore blood flow by capturing and removing clots from blocked arteries in the brain. The shape memory property allows these devices to expand and conform to the clot’s shape, improving retrieval success rates and reducing the risk of complications.
The DAWN Trial demonstrated that patients treated with Nitinol-based stent retrievers for ischemic stroke had a 49% rate of functional independence at 90 days, compared to only 13% in patients who received standard care alone, underscoring the life-saving impact of these devices.
5. Heart Valve Frames
Transcatheter heart valve replacements rely on Nitinol frames for their flexibility and self-expanding capabilities. These frames support the artificial valve and allow for minimally invasive implantation. The ability to deploy the valve through a catheter and expand it at the target site makes Nitinol-based heart valves a revolutionary advancement in treating conditions like aortic stenosis, especially in high-risk surgical patients.
The PARTNER 3 Trial showed that patients who received a Nitinol-based transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) had a 1.0% mortality rate at one year compared to 2.5% for those undergoing open-heart surgery, proving the effectiveness of Nitinol in reducing procedural risks.
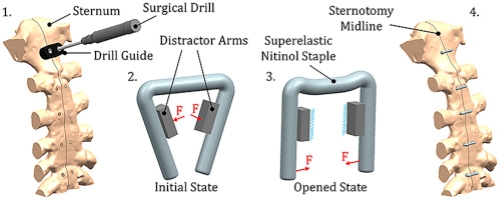
6. Bone Fixation and Implants
Orthopedic applications of Nitinol include bone plates, staples, and intramedullary implants. Its shape memory property enables compression in bone fractures, promoting faster and more stable healing. Additionally, Nitinol’s superelastic behavior helps maintain fixation while accommodating natural bone movement. These devices are particularly useful in spinal surgeries and small joint repairs.
A study in The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery reported that patients with Nitinol bone staples experienced 40% faster healing times in ankle fracture repairs compared to traditional titanium fixation methods, showcasing the efficiency of Nitinol-based orthopedic implants.[4]
 [5]
[5]
Fig. 3 Nitinol Bone Staples
Conclusion
Nitinol’s exceptional properties have transformed the medical device industry. Its superelasticity, shape memory, and biocompatibility make it an invaluable material in modern healthcare, enabling advancements in minimally invasive procedures, vascular interventions, and orthopedic applications. As research continues, Nitinol’s role in medical technology is expected to expand. For more medical applications and related cases, please check Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM).
Reference:
[1] Sabeti S, Schillinger M, Amighi J, Sherif C, Mlekusch W, Ahmadi R, Minar E. Primary patency of femoropopliteal arteries treated with nitinol versus stainless steel self-expanding stents: propensity score-adjusted analysis. Radiology. 2004 Aug;232(2):516-21. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2322031345. PMID: 15286322.
[2] Hong, J.T., Kim, T.J., Hong, S.N. et al. Uncovered self-expandable metal stents for the treatment of refractory benign colorectal anastomotic stricture. Sci Rep 10, 19841 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76779-8
[3] Wang Y, Liu C, Jian F, McIntyre GT, Millett DT, Hickman J, Lai W. Initial arch wires used in orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 31;7(7):CD007859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007859.pub4. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Feb 06;2:CD007859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007859.pub5. PMID: 30064155; PMCID: PMC6513532.
[4] Dock, Carissa & Freeman, Katie & Coetzee, J. & Stone McGaver, Rebecca & Giveans, M.. (2020). Outcomes of Nitinol Compression Staples in Tarsometatarsal Fusion. Foot & Ankle Orthopaedics. 5. 247301142094490. 10.1177/2473011420944904.
[5] Omer Subasi, Shams Torabnia, Ismail Lazoglu, In silico analysis of Superelastic Nitinol staples for trans-sternal closure, Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, Volume 107, 2020, 103770, ISSN 1751-6161, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1751616120303246