Lithium-Sulfur Batteries vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Comparative Analysis
Introduction
Electric vehicles (EVs) are on the brink of a major transformation, and at the heart of this revolution are lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries. These innovative power sources are poised to redefine the future of EVs by offering a range of distinct advantages over traditional lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. In this article, we delve into the compelling advantages that Li-S EV batteries have over Li-ion batteries, propelling us toward a cleaner and more sustainable mode of transportation.
Understanding Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries, or Li-ion batteries, are the standard power source for a wide range of portable electronic devices. These batteries operate based on the movement of lithium ions between the positive (cathode) and negative (anode) electrodes. During discharge, lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode, generating electrical energy. Thanks to their remarkable attributes, such as high energy density, extended cycle life, and relatively lightweight composition, Li-ion batteries have emerged as the dominant choice for electric vehicle (EV) batteries.
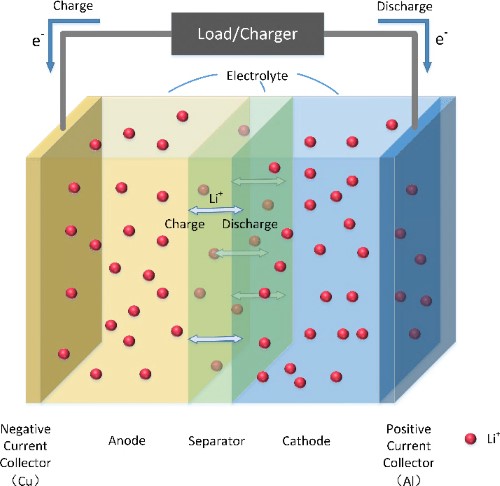 [1]
[1]
Figure 1. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
Understanding Lithium-Sulfur (Li-S) Batteries
However, lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries emerged as a promising alternative to the conventional lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, and they are commonly used in EVs. Li-S batteries use a different electrochemical reaction compared to Li-ion batteries. Namely, sulfur serves as the cathode, and lithium metal or lithium-ion serves as the anode. Li-S batteries come with higher energy density, lighter weight, and reduced production costs compared with Li-ion batteries, making them attractive for electric vehicles and other applications.
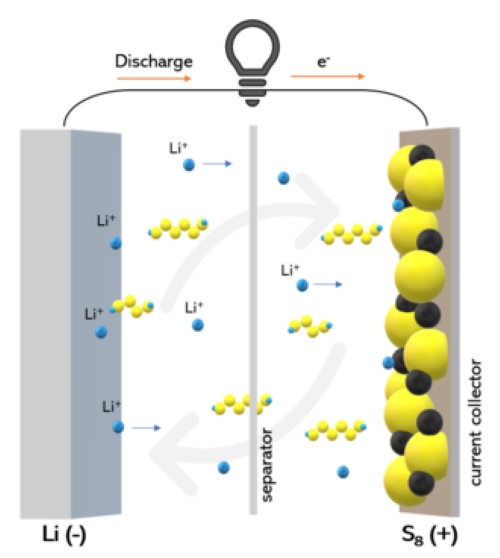 [2]
[2]
Figure 2. Lithium-Sulfur (Li-S) Batteries
Lithium-sulfur Batteries vs. Lithium-ion Batteries
Let’s continue by listing the respective strengths, and weaknesses of Li-S batteries and Li-ion batteries, and their potential to influence the future of electric vehicles.
1. Unprecedented Energy Density:
Li-S batteries boast an impressive theoretical energy density that surpasses that of Li-ion batteries. This is to say, Li-S EVs can potentially store more energy within the same volume or weight constraints, resulting in significantly longer driving ranges.
2. Lightweight Efficiency:
Sulfur, a key component of Li-S batteries, is not only abundant but also lightweight. This lightweight nature translates into reduced overall vehicle weight, enhancing energy efficiency. Li-S batteries contribute to lighter EVs, which in turn require less energy to move, leading to increased efficiency and extended battery life.
3. Quick Charging Capability:
One of the standout features of these batteries is their potential for rapid charging. Their high conductivity allows for faster charging times, making pit stops for charging akin to refueling with traditional fossil fuels. The convenience of quick charging addresses one of the primary concerns of EV drivers: range anxiety.
4. Reduced Cost:
Sulfur is an inexpensive material, which can potentially lead to lower production costs for Li-S batteries compared to lithium-ion batteries, which use materials like cobalt that can be expensive and subject to supply chain issues.
5. Environmental Friendliness:
Li-S batteries have the potential to be more environmentally friendly than their Li-ion counterparts. Sulfur is an abundant and cost-effective material, and its extraction and processing are less resource-intensive compared to materials like cobalt used in Li-ion batteries. Additionally, the simplified composition of Li-S batteries could facilitate easier recycling and a reduced environmental footprint.
6. Cycle Life:
Nevertheless, Li-ion batteries tend to have a longer cycle life compared to Li-S batteries. Li-S batteries have historically suffered from a shorter lifespan, primarily due to the dissolution of sulfur in the electrolyte during charge and discharge cycles. Researchers are actively working to improve the cycle life of Li-S batteries.
7. Safety:
Li-ion batteries have a track record of safety in EV applications. Li-S batteries, on the other hand, have faced safety challenges, including issues related to the formation of lithium sulfide, which can be unstable. Ensuring the safety of Li-S batteries remains a critical focus for research and development.
Related reading: An Overview on Lithium Applications
Conclusion
In summary, the advantages of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) EV batteries are poised to revolutionize the world of electric vehicles. With their exceptional energy density, lightweight efficiency, reduced cost, quick charging capabilities, and environmental friendliness, they offer a compelling alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries. As research and development in this field continue to progress, Li-S batteries are charging ahead, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future of electric mobility.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a leading supplier of various products, including Li-ion batteries and a variety of advanced batteries. Send us an inquiry if you are interested.
Reference:
[1] An Overview on Thermal Safety Issues of Lithium-ion Batteries for Electric Vehicle Application - Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Schematic-of-the-Lithium-ion-battery_fig2_324929541 [accessed 7 Sep 2023]
[2] Lithium–sulfur battery. (2023, August 20). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lithium%E2%80%93sulfur_battery