Hyaluronic Acid for Osteoarthritis
Introduction
Osteoarthritis is a joint disease that influences millions of people around the world. One of the most common sites of osteoarthritis is the knee joint, with symptoms of pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Hyaluronic acid (HA) has been widely used as a treatment for osteoarthritis due to its ability to reduce pain and improve joint function. In this article, we will discuss the mechanism and effectiveness of hyaluronic acid treatment for osteoarthritis. Hope that you can have a further comprehension of the properties and therapeutic applications of hyaluronic acid.
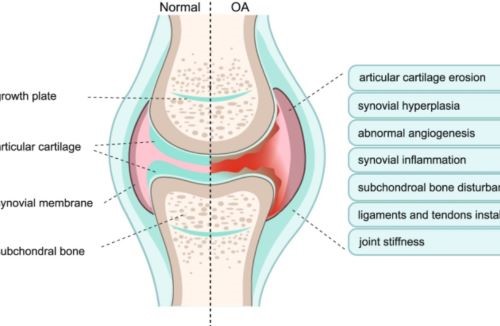
Figure 1. Osteoarthritis
Benefits of Hyaluronic Acid for Osteoarthritis Treatment
Hyaluronic acid is a natural substance with hydrating and lubricating effects. You can find this material in the human body, including the umbilical cord, vitreous body, dermis, and synovial fluid. For one thing, these substances could attract millions of water molecules, leading to supple and plump skin. For another, HA could reduce friction and outside pressure, thus protecting our knees and hips.
Namely, HA supplementations and injections are particularly beneficial for osteoarthritis treatment. The high concentrations of hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid lubricate and cushion the joints. Yet, in the osteoarthritic knee, the reduced level of hyaluronic acid is replenished with these HA injections. Joint pain, inflammation, cartilage damage, and other symptoms are reduced as well.
Related reading: What Does Hyaluronic Acid Do For Joints?
Mechanisms of Hyaluronic Acid Used for Osteoarthritis
The exact mechanisms of hyaluronic acid treatment are complex and multifactorial. It is likely that the combination of HA's lubricating, anti-inflammatory, and chondroprotective properties contributes to its therapeutic effect.
--Cushioning Effect
Let’s learn about the specific mechanisms of HA treatment and related studies. One theory is that hyaluronic acid acts as a cushion and protects joints against friction and damage. This protective effect is achieved by HA’s large and complex molecules, which create a cushioning effect that reduces the pressure on the joint surfaces, ultimately alleviating pain and improving joint functions. Also, HA injections provide a physical barrier that reduces friction between the joint surfaces.
--Anti-inflammation Function
Another theory is that HA injections have anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a key factor in the development and progression of osteoarthritis. HA molecules can bind to receptors on immune cells and inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines, which can reduce inflammation in the joint and alleviate pain.
--Chondroprotective Effect
In addition to its lubricating and anti-inflammatory features, hyaluronic acid possesses a chondroprotective effect. Chondrocytes are the cells that produce and maintain the cartilage in the joint. In osteoarthritis, the chondrocytes can become damaged or die, resulting in cartilage loss and joint degeneration. HA injections have been shown to stimulate the production of extracellular matrix molecules by chondrocytes, which can promote the repair and regeneration of the cartilage.
Efficacy of Hyaluronic Acid Employed for Osteoarthritis
Several clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of HA injections in the treatment of osteoarthritis of knees and hips.
- A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found that HA injections were useful in reducing pain and improving joint function compared to placebo injections. The effect of HA treatment was sustained for up to 6 months after treatment. [1]
- Studies also showed that hyaluronic acid not only has pain-relieving effects but also has a potential structure-modifying function. Besides, it was observed that the synovial inflammation was significantly reduced and the chondrocyte density and vitality were improved. [2]
Conclusion
In a word, hyaluronic acid treatment is a widely used therapy for osteoarthritis. The mechanisms of action for HA treatment involve its lubricating, anti-inflammatory, and chondroprotective properties. Several clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of HA injections in reducing pain and improving joint functions in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Further researches are needed to fully understand the mechanisms of HA treatment and to optimize its use in the clinical setting.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) has rich experience in the manufacturing and sale of hyaluronic acid. Medical-grade, cosmetic-grade, injection-grade, and food-grade HAs are available on our website. High molecular weight, middle molecular weight, and low molecular weight hyaluronic acids are also available. For more detailed information, please check our homepage.
References:
[1] Migliore A, Procopio S. Effectiveness and utility of hyaluronic acid in osteoarthritis. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2015 Jan-Apr;12(1):31-3. doi: 10.11138/ccmbm/2015.12.1.031. PMID: 26136793; PMCID: PMC4469223.
[2] Frizziero L, Govoni E, Bacchini P. Intra-articular hyaluronic acid in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: clinical and morphological study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1998 Jul-Aug;16(4):441-9. PMID: 9706425.