What is Lanthanum Hexaboride Electrode
Introduction
Lanthanum hexaboride (LaB6), with its distinctive purple powder form, holds immense potential to revolutionize various industries. This compound, represented by the molecular formula LaB6, showcases exceptional properties that make it a sought-after material in cutting-edge applications.

Lanthanum Hexaboride Synthesis
The synthesis of LaB6 involves dissolving lanthanum trioxide and borax in a suitable molten salt, followed by electrolysis with graphite anodes at high temperatures. This process deposits LaB6 on graphite or steel cathodes. Notably, its insolubility in water, hydrochloric acid, and its magenta solid form contribute to its stability.
Applications in Nuclear Fusion and Thermoelectric Power Generation
Due to its remarkable melting point and thermal radiation performance, LaB6 emerges as a promising alternative to high melting point metals and alloys in nuclear fusion reactors and thermoelectric power generation systems. Its ability to withstand extreme conditions positions it as a crucial component in advancing these technologies.
Electron-Emitting Cathodes
One of the primary applications of LaB6 lies in the fabrication of electron-emitting cathodes, particularly in the creation of specially structured crystals. The unique property of low electron emission allows for the development of cathode materials with maximum emission currents at medium temperatures. High-quality single crystals of LaB6 become ideal materials for high-power electron emission cathodes, contributing to advancements in electron microscope technologies.
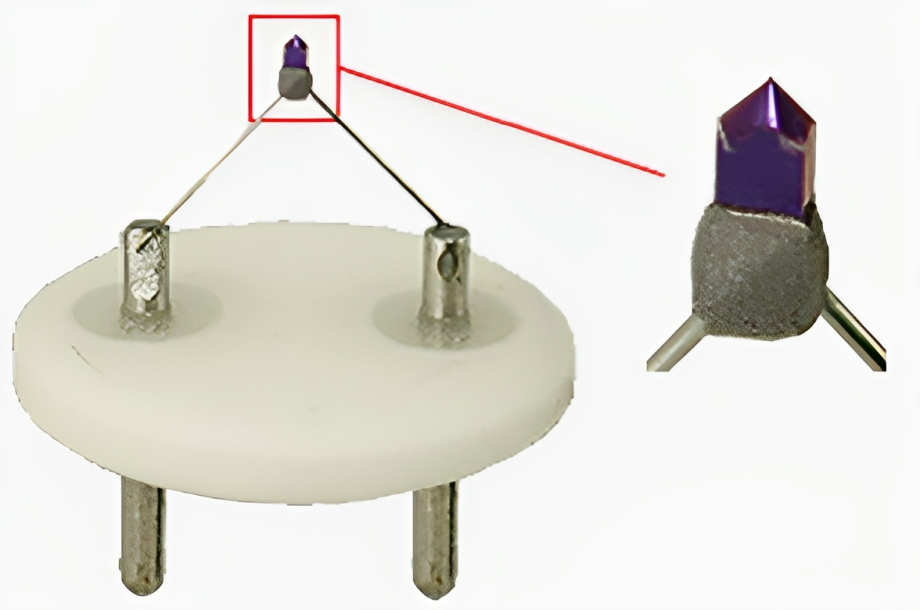
Versatility in Electron Beam Systems
The exceptional overall performance of LaB6 extends its influence to various electron beam systems. From electron beam engraving and heat sources to torches and accelerators, LaB6 plays a pivotal role in manufacturing high-performance components for diverse applications.
Wide-Scale Applications
The versatile nature of LaB6 finds successful applications across a myriad of sectors, including radar aerospace, electronics, instrumentation, medical equipment, home appliances, metallurgy, and environmental protection. Its adaptability is evident in products offered as powders, polycrystalline structures, and single crystals.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Lanthanum Hexaboride, with its unique synthesis process and outstanding properties, stands as a beacon of innovation in advanced technologies. From enhancing electron-emitting cathodes to facilitating breakthroughs in nuclear fusion and thermoelectric power generation, LaB6 proves to be an indispensable material across a spectrum of high-tech fields. As we delve further into the realm of possibilities, the applications of Lanthanum Hexaboride are poised to redefine the landscape of modern technology.
As a leading provider of advanced materials, Stanford Advanced Materials takes pride in contributing to the utilization and understanding of compounds like LaB6, fostering advancements in various technological domains.