The 10 Strongest Materials Known To Man
1. Graphene
Brief introduction
Graphene is a honeycomb two-dimensional film formed by carbon atoms with sp2 hybridization. It is a monolayer sheet structure separated from graphite, and it is also the thinnest new material currently known. The tensile strength and elastic modulus of graphene are 125Gpa and 1.1tpa, respectively, and its strength is 100 times that of ordinary steel. Bags made of graphene, which can hold about 2 tons of weight, are by far the strongest material known.

Growing trend
Since the Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded in 2010, the number of global graphene patent applications has increased dramatically. It is expected to be applied in many fields in the future, such as electronics, energy storage, catalysts, sensors, optoelectronic transparent thin films, super-strength composite materials, and biological medicine.
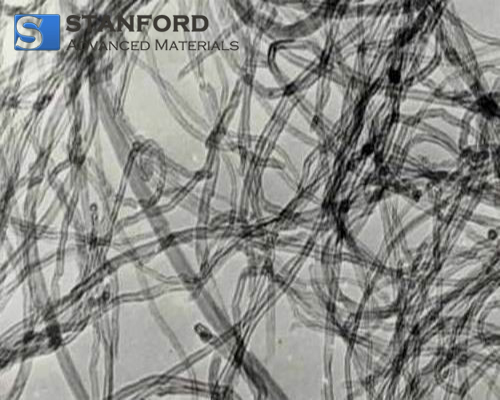
2. Carbon Nanotube
Brief introduction
Carbon nanotubes (CNTS) are a kind of one-dimensional quantum material with the hexagonal arrangement of carbon atoms forming coaxial circular tubes from several layers to dozens of layers, and it can be divided into single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) according to the number of layers of graphene sheets. Carbon nanotubes have excellent mechanical properties, with a tensile strength of 50 ~ 200GPa, which is 100 times that of steel, but the density is only 1/6 of that of steel. Besides, its elastic modulus can reach up to 1TPa, which is equivalent to that of diamond and about 5 times that of steel.

Growing trend
Since its discovery in the 1990s, the carbon nanotube-related industry has boomed, and it is widely used to make composite materials and films, transparent conductors, thermal interfaces, body armor, wind turbine blades, electrodes for functional devices, and catalyst carriers.
3. Metallic Glass
Brief introduction
Metallic glass is also called amorphous metal, which is usually an alloy, with an amorphous structure and glass structure. This double structure determines that it has many properties beyond the reach of crystalline metal and glass, such as good electrical conductivity, high strength, high elasticity, more wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant. Metallic glass is stronger than steel and harder than hard tool steel.

Growing trend
Metallic glass has super strength, elasticity, and magnetic properties, and can remain solid without crystallizing at high temperatures, which is mainly used in aerospace and military weapons.
4. Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber (UHMWPE)
Brief introduction
UHMWPE is a kind of fiber made from polyethylene with a relative molecular weight of 1 million to 5 million, which is currently the strongest and lightest fiber in the world. It is 15 times stronger than steel wire but very light in weight, and it is 40 percent lighter at most than materials such as aramid.

Growing trend
UHMWPE is widely used in rope, mooring and rope nets to life protection applications, high-performance textiles, composites, laminated materials. It is estimated that the annual world demand for UHMWPE will be 60, 000 tons in the next five years and 100, 000 tons in the next 10 years.
5. Boron Nitride Nanotubes
Brief introduction
Like carbon, boron nitride can form single-atom sheets that can be curled up to form nanotubes. The boron nitride nanotubes themselves are as strong as carbon nanotubes, but the real advantage comes from their ability to stick firmly to the polymer as it binds to the polymer. The strength of boron nitride nanotubes is higher than that of carbon nanotubes, about 30% higher than PMMA interface, and about 20% higher than epoxy resin.

Growing trend
Boron nitride nanotubes have optical properties, excellent mechanical and thermal conductivity properties, as well as withstand high temperatures and absorb neutron radiation, thus becoming effective additives for mechanical or thermal enhancement of polymer, ceramic and metal composites. Additional applications of boron nitride nanotubes include protective shields, electrical insulators, and sensors.
6. Lonsdaleite
Brief introduction
The Lonsdale stone was discovered in a crater by American geologist Lonsdale and defined as a hexagonal meteorite diamond. Like diamonds, they are made of carbon atoms, but their carbon atoms are arranged in different shapes. The results of the simulation show that the Lonsdale stone is 58% more resistant to pressure than the diamond.

7. Diamond
Brief introduction
Diamond is the hardest substance found on earth in so many natural forms, and it is an allotrope of carbon. The hardness of diamond is the highest level of Mohs hardness - grade 10. Its microhardness is 10000kg/mm2, which is 1,000 times higher than quartz and 150 times higher than corundum.

Growing trend
Diamond is widely used in industry, mainly in the diamond cutter, diamond for drawing die, the diamond bit.
8. Aerogel
Brief introduction
Aerogel is a form of solid material that has the smallest density in the world. Aerogels are very strong and durable and can withstand pressure thousands of times their mass, and they don't melt until it reaches 1200 degrees Celsius.

Growing trend
Aerogels show many unique properties in the fields of thermal, optical, electrical, mechanical and acoustic, which can be used as thermal insulation materials, ICF and X-ray laser target, catalyst, adsorbent, various electronic devices and so on.
9. Silicon carbide
Brief introduction
Silicon carbide is a natural mineral in nature, or it is made from quartz sand, petroleum coke (or coal coke), wood chips and other raw materials by smelting at high temperature in a resistive furnace. Silicon carbide is hard with a Mohs hardness of 9.5, which is second only to the world's hardest diamond. In addition, silicon carbide has excellent thermal conductivity. It is a kind of semiconductor and can resist oxidation at high temperature.
![]()
Growing trend
As a typical representative of third-generation semiconductor materials, silicon carbide is favored by downstream semiconductor enterprises. Power electronic devices made of silicon carbide substrate and epitaxial material can work under high voltage and high-frequency environment with outstanding performance advantages and broad industrial prospects.
10. Darwin’s bark spider

Brief introduction
A new species of spider, Darwin's bark spider, has been found on Madagascar to create the world's largest and most solid web. At 25 meters wide, the spider's web is the strongest biological material ever studied and 10 times stronger than kevlar of the same size.
Thank you for reading our article. If you want to learn more about the strongest materials, we would like to advise you to visit Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) for more information.