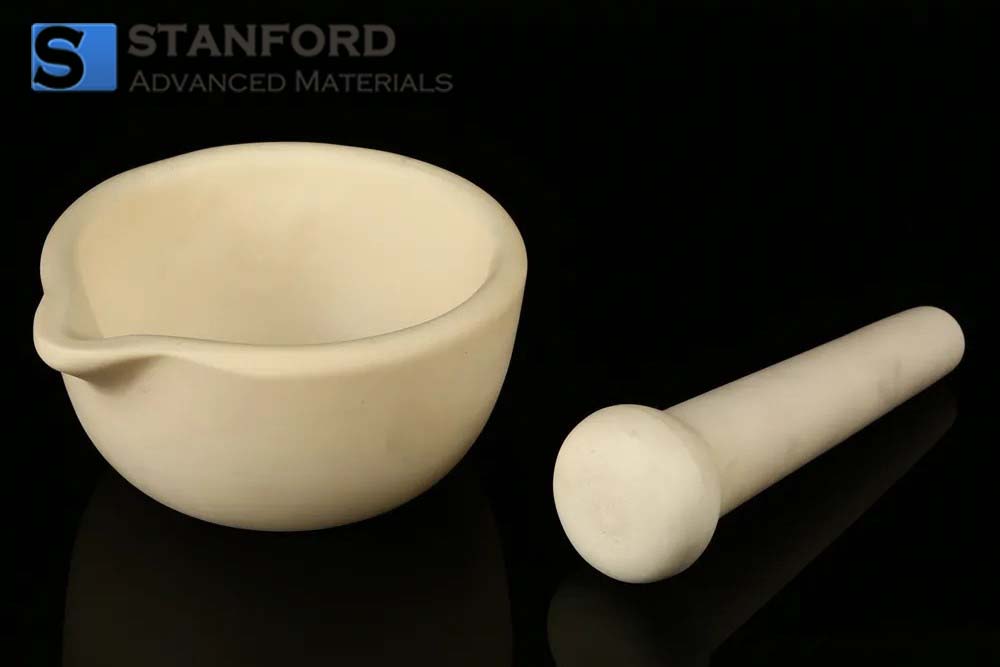
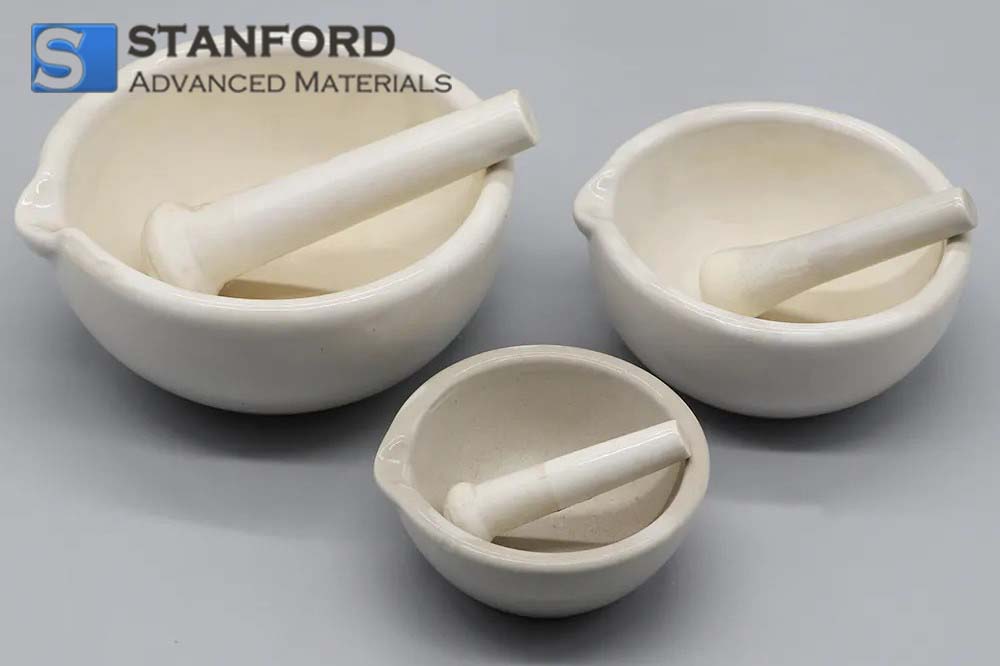
AC0924 Alumina Mortar and Pestle Set
| Catalog No. | AC0924 |
| Size | 30ml -500ml |
| Material | Al2O3 |
| Purity | 95% 99% 99.7% |
| Density | 3.8~3.9 g/cm3 |
| MSDS/SDS |
Alumina Mortar and Pestle with high purity has a great efficiency cost ratio. Stanford Advanced Materials provides alumina ceramic products with high purity, tight dimensional tolerance, and competitive prices, which can fulfill most of the requirements.
Related Products: Stainless Steel Mortar and Pestle, Zirconia Mortars & Pestles, Tungsten Carbide Mortar and Pestle
Description of Alumina Mortar and Pestle Set
An alumina mortar and pestle is a common laboratory tool used for grinding, mixing, and crushing solid substances. It consists of two components:
Alumina Mortar: The mortar is a bowl-shaped vessel usually made of high-purity alumina ceramic material. It has a smooth interior surface and sturdy construction that allows for efficient grinding and blending of materials.
Pestle: A pestle is a rod-shaped tool that fits inside the mortar. It is used to crush, grind, or mix substances by applying pressure and friction against the mortar's inner surface.
Specifications of Alumina Mortar and Pestle Set
|
Composition |
UNIT |
Al95 |
Al99 |
Al997 |
|
Al2O3 Content |
% |
95 |
99 |
99.7 |
|
Color |
|
White |
Ivory |
Ivory |
|
Tensile Strength |
Kpsi |
32 |
38 |
36 |
|
Flexural Strength |
Kpsi |
52 |
55 |
54 |
|
Compressive Strength |
Kpsi |
300 |
377 |
350 |
|
Density |
g/cc |
3.70 |
3.90 |
3.92 |
|
Hardness |
HV, GPa |
13.8 |
17.2 |
18 |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
W/(m K) |
25 |
30 |
30 |
|
C.O.T.E. |
In / In°C (x10^-6) |
7.7 |
7.8 |
7.8 |
|
Working Temperature |
°C |
1500 |
1650 |
1750 |
|
Dielectric Constant |
|
9.5 |
9.7 |
9.8 |
|
Volume Resistivity (25°C) |
Ohm-cm |
>10^14 |
>10^14 |
>10^14 |
Customization is available.
Applications of Alumina Mortar and Pestle Set
1. Pharmaceuticals: Used for grinding and mixing medications, ensuring homogeneity and fine particle size for better absorption and efficacy.
2. Laboratories: Essential in chemical and biological laboratories for grinding, mixing, and homogenizing samples, ensuring consistent and reproducible results in experiments.
3. Material Science: Employed in the preparation of samples for analysis, including grinding materials to a fine powder for X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and other analytical techniques.
4. Food Industry: Used for grinding spices, herbs, and other food ingredients to release flavors and aromas, ensuring uniform texture and quality in culinary applications.
5. Ceramics and Glass: Utilized in the preparation of ceramic and glass powders, enabling precise control over particle size and distribution for manufacturing high-quality products.
6. Chemical Synthesis: Important in chemical synthesis and formulation, allowing for the thorough mixing of reactants and catalysts to ensure complete reactions and high yields.
7. Cosmetics: Used in the preparation of cosmetic powders and formulations, ensuring a uniform consistency and texture for products like face powders and creams.
8. Educational Purposes: Common in educational settings for teaching students about material preparation, mixing, and homogenization techniques in chemistry and biology courses.
9. Metallurgy: Applied in metallurgical laboratories for preparing metal powders and alloys, facilitating the study of material properties and behaviors.
10. Environmental Science: Used in environmental testing and analysis, such as preparing soil and sediment samples for chemical analysis to determine pollutant levels and composition.
11. Nanotechnology: Employed in the preparation of nanoparticles and nanocomposites, where precise grinding and mixing are crucial for achieving the desired particle size and distribution.
Packaging of Alumina Mortar and Pestle Set
Our Alumina mortar and pestle sets are carefully handled to prevent damage during storage and transportation and to preserve the quality of our products in their original condition.
Prototyping service also available for other ceramics material
LATEST RECOMMENDED
GET A QUOTE
Send us an Inquiry now to find out more Information and the latest prices,thanks!