6 Common Uses of Titanium Dioxide Pigment
Introduction
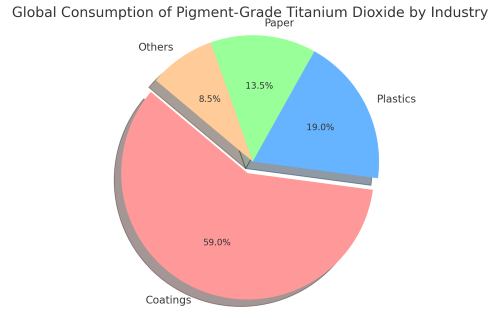
Titanium dioxide (TiO₂) is one of the most efficient white pigments extensively used across various industries. Its applications span numerous sectors of the global economy, making it an indispensable material in the production of white or light-colored products. The primary industries utilizing TiO₂ pigments include coatings, plastics, and paper, which together account for the majority of its global consumption. Here’s a closer look at the main applications:

1. Coatings
The coatings industry is the largest consumer of titanium dioxide pigments, accounting for approximately 58% to 60% of the global consumption of TiO₂ pigments. Coatings encompass a broad range of products, including paints, varnishes, and finishes. These products can be solvent-based or water-based and include powder coatings and UV-cured coatings.
Titanium dioxide is the most widely used pigment in the coatings industry due to its excellent properties. It provides bright and vivid colors, high opacity, strong tinting strength, and superior weather resistance. These attributes make coatings produced with TiO₂ more durable and effective at protecting and decorating surfaces. The primary applications of TiO₂ pigments in coatings include:
- Automotive Coatings: Used for both aesthetic and protective purposes.
- Architectural Coatings: Includes paints for buildings and structures, with latex paints being a significant segment.
- Industrial Coatings: Applied to machinery, appliances, and other equipment.
- Marine Coatings: Used on ships and offshore structures for protection against harsh marine environments.
- Specialty Coatings: Includes coatings for toys, household items, and decorative objects.
Related reading: Everything You Need to Know About Titanium Oxides
2. Plastics
Plastics are the second largest market for titanium dioxide, consuming about 18% to 20% of the global supply. In plastics, TiO₂ pigment is valued for its ability to enhance whiteness, opacity, and UV resistance. It helps improve the heat and light stability of plastic products, preventing degradation from UV exposure. Its fine particle size and uniform distribution enhance the quality of the plastic by providing better reflectivity of light and improved mechanical properties.
Common applications of TiO₂ pigments in plastics include:
- Packaging: Films, bottles, and containers that require high opacity and aesthetic appeal.
- Construction Materials: Pipes, sidings, and fittings that benefit from enhanced durability.
- Consumer Goods: Household items, toys, and electronic housings.
- Automotive Parts: Interior and exterior plastic components.
3. Paper
Titanium dioxide is the third most significant application area for TiO₂ pigments, particularly in the United States, where it is the second largest market. In the paper industry, TiO₂ is used to improve the brightness, opacity, and printability of paper. It is essential in producing high-quality paper products, including:
- Fine Papers: Used in books, magazines, and high-quality printing materials.
- Thin Papers: Such as those used in dictionaries and high-end magazines.
- Specialty Papers: Including banknotes, computer paper, and decorative papers.
The use of TiO₂ in paper results in superior whiteness, gloss, and smoothness, enhancing the overall quality and usability of the paper.
4. Rubber
In the rubber industry, titanium dioxide is used not only as a pigment but also for its reinforcing and filler properties. It helps improve the durability, aging resistance, and mechanical strength of rubber products. TiO₂ is particularly important in:
- Tires: Especially the white sidewalls of car tires.
- Footwear: Including sports shoes and rubber boots.
- Rubber Flooring: Providing color and strength to flooring materials.
- Miscellaneous Products: Such as gloves, raincoats, and sporting goods.
5. Chemical Fibers
Titanium dioxide is crucial in the chemical fiber industry, particularly for synthetic fibers. It serves as a delustering agent, reducing the shine of fibers by scattering light. This is essential for producing fibers with a matte finish. Synthetic fibers, including nylon, polyester, and rayon, benefit from the inclusion of TiO₂ due to its high refractive index and optimal particle size distribution.
6. Inks
In the ink industry, titanium dioxide pigment is a vital component due to its high opacity and tinting strength. It is used in various types of inks, including those used for printing newspapers, books, magazines, and packaging materials. TiO₂ ensures high-quality prints with excellent color consistency and durability. Specific uses include:
- White and Light-Colored Inks: Providing opacity and brightness.
- Specialty Inks: Used for printing on metals, ceramics, and plastics.
Other Applications
Beyond the major industries, titanium dioxide also finds applications in:
Fields | Benefits | Uses |
Coatings | High opacity, strong tinting, weather resistance | Automotive, Architectural, Industrial, Marine, Specialty |
Plastics | Enhances whiteness, UV resistance, stability | Packaging, Construction, Consumer Goods, Automotive |
Paper | Improves brightness, opacity, printability | Fine Papers, Thin Papers, Specialty Papers |
Rubber | Reinforcement, durability, aging resistance | Tires, Footwear, Flooring, Miscellaneous |
Chemical Fibers | Reduces shine, enhances matte finish | Synthetic Fibers (Nylon, Polyester, Rayon) |
Inks | High opacity, color consistency, durability | White, Light-Colored, Specialty Inks |
- Cosmetics: Providing whiteness and opacity in products like foundations and sunscreens.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used in tablet coatings and as a pigment in some medications.
- Food Additives: Serving as a colorant in certain food products.
- Educational Supplies: Used in art supplies such as paints, crayons, and markers.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) offers a comprehensive range of high-quality Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) products at competitive prices, tailored for various applications. Our product line includes:
- Photocatalytic Nano TiO₂: For environmental purification and self-cleaning surfaces.
- Nano TiO₂ for Lithium Batteries: Enhances performance and stability.
- Nano TiO₂ for Ceramics: Improves strength and durability.
- Anatase and Rutile TiO₂: Suitable for diverse industrial applications.
These products leverage the excellent properties of TiO₂, making them essential for industries such as coatings, plastics, paper, rubber, chemical fibers, and inks.
Conclusion
In summary, titanium dioxide pigment is an essential material across numerous industries. Its superior properties make it the preferred choice for enhancing color, opacity, and durability in a wide range of products, ensuring its continued importance in the global market.