- Products
- Categories
- Blog
- Podcast
- Application
- Document
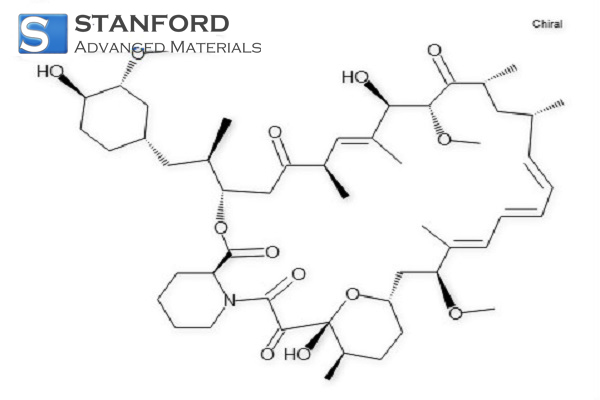
HA4819 Rapamycin Powder, CAS 53123-88-9
| Catalog No. | HA4819 |
| Synonyms | Sirolimus, RAPA |
| Keywords | Immunosuppressor, anti-aging, cancer |
Rapamycin is used in clinical settings to prevent rejection in organ transplantation and to treat certain types of cancer.
Related products: Metformin (Hydrochloride), Acarbose, Dasatinib Monohydrate
INQUIRY
Add to Inquiry List
Description
Specification
LATEST RECOMMENDED

OM2279 2-(4-Bromophenyl)-4, 6-Diphenyl-1, 3, 5-Triazine Powder

OM2280 2-(Methylthio) Pyridine-3-Boronic Acid Powder

OM2281 2,7-Dihydroxynaphthalene Powder

OM2282 2-Bromophenylboronic Acid Powder

OM2284 2-Naphthalene Boronic Acid Powder

OM2286 Linezolid Related Compound D Powder

OM2287 Trans-4-(Aminomethyl) Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid Powder
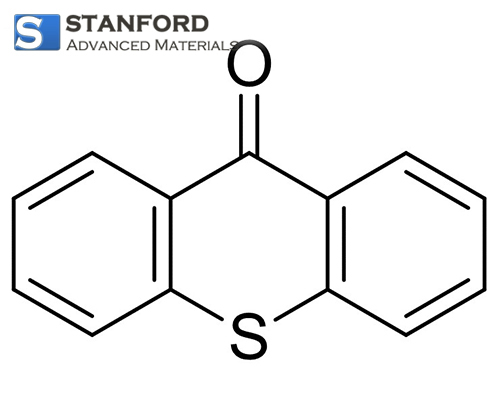
OX3596 Thioxanthen-9-one (CAS No. 492-22-8)
GET A QUOTE
Send us an Inquiry now to find out more Information and the latest prices,thanks!