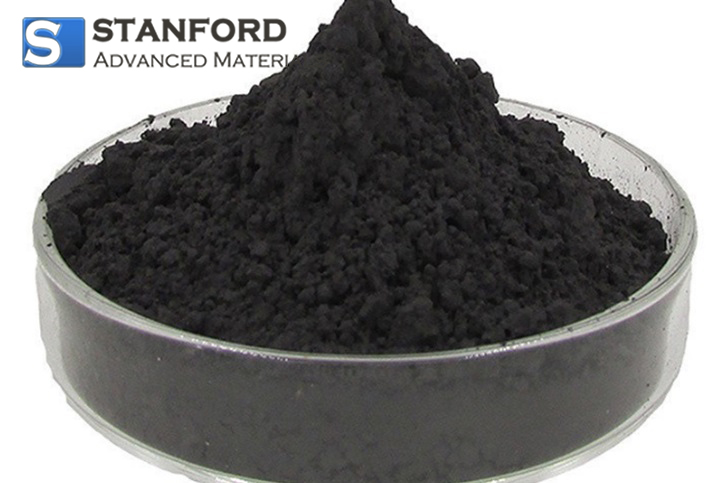
WM0146 Tungsten Powder (W Powder)
| Catalog No. | WM0146 |
| Size | 1-10μm -100mesh to +325mesh |
| Material | W |
| Purity | W≥99.95% |
| Appearance | dark gray powder |
| CAS Number | 7440-33-7 |
| APS | 0.5-45.0 μm or customized |
| MSDS/SDS |
Tungsten Powder (W Powder) is a dark gray powder with the chemical formula W. Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a global supplier of high-quality Thermal Spraying Powder, specializing in the provision of high-purity Tungsten Powder.
Related products: Spherical Tungsten Powder, Nano Tungsten Powder, Tungsten Carbide Powder, Micro Tungsten Carbide Powder
Tungsten Powder Description
Tungsten Powder, with its versatile properties, holds a pivotal role in numerous industries. Its remarkable density makes it a crucial component in manufacturing heavy alloys like tungsten carbide, essential for applications such as cutting tools, mining equipment, and armor-piercing projectiles. Moreover, its exceptional heat resistance and conductivity contribute to its widespread use in producing electrical and electronic components, including filaments for light bulbs and heating elements. Additionally, Tungsten Powder plays a vital role in crafting radiation shielding materials crucial for medical and industrial applications.

Tungsten Powder Specification
|
Specification |
Grade |
APS/BET/FSSS |
Oxygen (%,≯) |
|
Ultra-Fine Size |
ZE03 |
3.1-5.2m2/g |
0.60 |
|
ZE04 |
2.0-3.5m2/g |
0.55 |
|
|
ZE06 |
0.50-0.70μm |
0.40 |
|
|
ZE07 |
0.60-0.80μm |
0.35 |
|
|
ZE08 |
0.70-0.90μm |
0.25 |
|
|
Fine Size |
ZW10 |
0.90-1.10μm |
0.20 |
|
ZW12 |
1.10-1.30μm |
0.15 |
|
|
ZW15 |
1.30-1.70μm |
0.12 |
|
|
Medium Size |
ZW20 |
1.80-2.20μm |
0.08 |
|
ZW25 |
2.30-2.70μm |
0.08 |
|
|
ZW30 |
2.80-3.20μm |
0.06 |
|
|
ZW35 |
3.30-3.70μm |
0.06 |
|
|
ZW40 |
3.80-4.50μm |
0.04 |
|
|
ZW50 |
4.50-5.50μm |
0.04 |
|
|
ZW60 |
5.50-6.50μm |
0.04 |
|
|
ZW70 |
6.50-7.50μm |
0.04 |
|
|
Coarse Size |
ZW80 |
7.50-8.50μm |
0.04 |
|
ZW90 |
8.50-9.50μm |
0.04 |
|
|
ZW100 |
9.00-11.0μm |
0.04 |
|
|
ZW120 |
11.0-13.0μm |
0.03 |
|
|
Ultra-Coarse Size |
ZW150 |
13.0-17.0μm |
0.03 |
|
ZW200 |
16.0-25.0μm |
0.03 |
|
|
ZW300 |
25.0-35.0μm |
0.03 |
|
|
ZW400 |
35.0-45.0μm |
0.03 |
|
Impurities (ppm, ≯) |
|||||||||
|
Al |
As |
Bi |
Ca |
Cd |
Co |
Cr |
Cu |
Fe |
K |
|
5 |
10 |
1 |
15 |
1 |
10 |
20 |
3 |
50 |
15 |
|
Mg |
Mn |
Mo |
Na |
Ni |
P |
Pb |
S |
Sb |
Si |
|
10 |
10 |
30 |
15 |
20 |
10 |
1 |
10 |
5 |
15 |
|
Sn |
Ti |
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
10 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tungsten powder Application
1. Heavy Alloys: Integral in manufacturing heavy alloys like tungsten carbide for cutting tools, mining equipment, and armor-piercing projectiles.
2. Electrical Components: Utilized in producing electrical and electronic components due to their exceptional heat resistance and conductivity, including filaments for light bulbs and heating elements.
3. Radiation Shielding: Essential in crafting radiation shielding materials for medical and industrial applications to protect against harmful radiation.
4. Additive Manufacturing: Used as a feedstock material in additive manufacturing processes, such as 3D printing, to produce intricate metal parts with high-density characteristics.
5. Ceramics and Refractories: Employed in producing tungsten-based ceramics and refractory materials for high-temperature applications, such as furnace linings and crucibles.
6. Metal Injection Molding (MIM): Utilized metal injection molding processes to produce complex metal parts with high precision and density for various industries, including automotive and aerospace.
7. Chemical Applications: Found in chemical processes as catalysts or additives for enhancing the properties of materials in industries such as petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Tungsten Powder (W Powder) Safety Information
|
Signal Word |
Danger |
|
Hazard Statements |
H228-H315-H319 |
|
RTECS Number |
YO7175000 |
|
Transport Information |
N/A |
|
WGK Germany |
3 |
|
GHS Pictograms |
 |
Tungsten Powder (W Powder) Packaging
Our Tungsten Powder (W Powder) is carefully handled during storage and transportation to preserve the quality of our product in its original condition.
Double plastic bags in the iron drum, 50kg/piece. Or according to the needs of customers.
Related articles:
LATEST RECOMMENDED







GET A QUOTE
Send us an Inquiry now to find out more Information and the latest prices,thanks!