Birefringence: Unveiling the Optical Properties of Crystals
Understanding Birefringence
What Is Birefringence
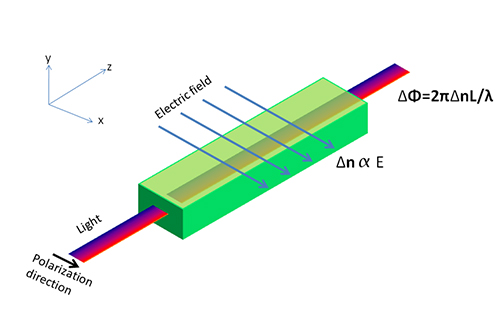
Birefringence, also known as double refraction, is an optical phenomenon where a material splits a light wave into two distinct rays. These rays, known as the ordinary and extraordinary rays, travel at different speeds and are polarized at perpendicular angles. This property is intrinsic to certain anisotropic materials, meaning their optical characteristics vary with direction.
How Birefringence Occurs in Materials
Birefringence arises from the internal structure of materials. In isotropic materials, light travels uniformly in all directions, resulting in a single refracted ray. However, in anisotropic materials, such as crystals, the molecular arrangement causes light to refract differently depending on its polarization and the material's internal axes. This variation leads to the separation of light into two rays, each following a unique path through the material.
Applications of Birefringence in Microscopy
Enhancing Material Analysis with Polarized Light
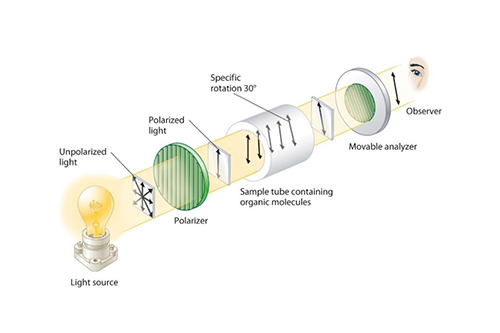
In microscopy, birefringence is a valuable tool for analyzing the optical properties of materials. Polarized light microscopes utilize polarized filters to examine the birefringent characteristics of samples. By observing the interference patterns and color changes caused by birefringence, scientists can identify stress patterns, molecular orientations, and compositional variations within materials.
Identifying Crystal Structures
Birefringence is particularly useful in identifying and studying crystal structures. Different crystals exhibit unique birefringent properties based on their symmetry and molecular arrangement. By analyzing the double refraction patterns under polarized light, researchers can determine the type of crystal, assess its quality, and investigate defects or inclusions within the crystal lattice.
Common Birefringence Materials
Birefringence is observed in a variety of natural and synthetic materials. Understanding which materials exhibit this property is essential for applications in optics, materials science, and engineering.
|
Material Type |
Examples |
Birefringent Properties |
|
Natural Crystals |
Calcite, Quartz, Tourmaline |
High birefringence with distinct double refraction |
|
Synthetic Crystals |
Sapphire, Lithium Niobate |
Controlled birefringence for optical devices |
|
Polymers |
Polycarbonate, Nylon |
Moderate birefringence used in stress analysis |
|
Biological Tissues |
Collagen, Muscle Fibers |
Birefringence reveals structural organization |
Techniques for Measuring Birefringence
Accurate measurement of birefringence is crucial for both research and industrial applications. Several techniques are employed to quantify this optical property.
Polarizing Microscopes
Polarizing microscopes are the most common instruments used to measure birefringence. By using polarized light and rotating the sample or the analyzer, subtle changes in light intensity and color can be observed. These observations allow for the determination of the material's birefringence magnitude and direction.
Interferometric Methods
Interferometric techniques, such as Michelson or Mach-Zehnder interferometers, provide precise measurements of birefringence by analyzing the interference patterns created by the split light rays. These methods are highly sensitive and can detect minute differences in refractive indices, making them ideal for advanced material characterization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes birefringence in crystals?
Birefringence in crystals is caused by their anisotropic molecular structure, which causes light to split into two rays with different refractive indices.
How is birefringence measured in materials?
Birefringence is typically measured using polarizing microscopes or interferometric methods that analyze the separation and phase difference of light rays passing through the material.
Can all crystals exhibit birefringence?
No, only anisotropic crystals with non-uniform molecular structures exhibit birefringence. Isotropic crystals do not show this property.
What are some common applications of birefringent materials?
Birefringent materials are used in optical devices like waveplates, polarizers, and in stress analysis within engineering materials.
How does birefringence affect microscopy analysis?
Birefringence enhances microscopy analysis by revealing internal stresses, molecular orientations, and crystal structures through the interaction of polarized light with the sample.