- Products
- Categories
- Blog
- Podcast
- Application
- Document
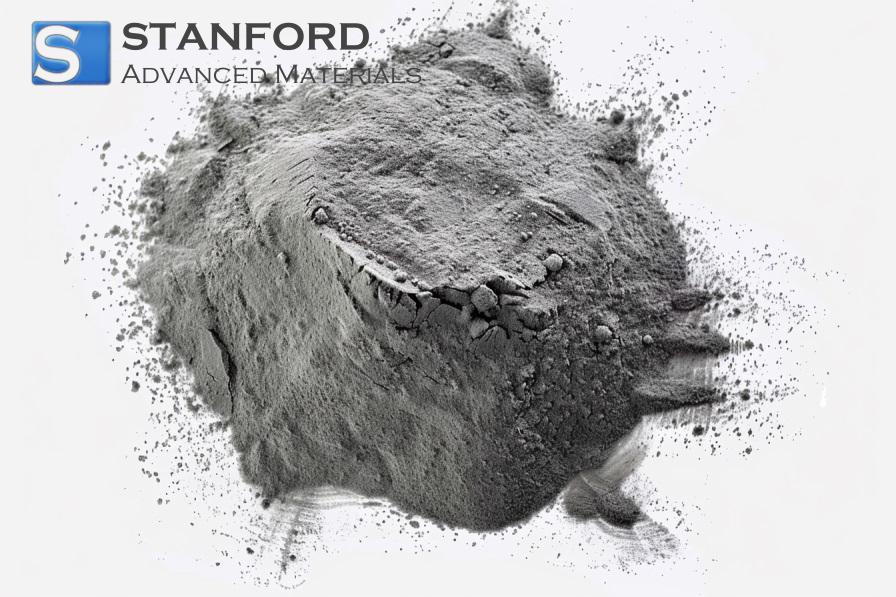
CD1110 Cadmium Metal (Cd Metal) (CAS No.7440-43-9)
| Catalog No. | CD1110 |
| CAS Number | 7440-43-9 |
| Purity | 99.999%, 99.9999%, 99.99999% |
| Density (at R.T.) | 8.65 g/cc |
| Physical Specifications | Powder / Particle / Block |
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a leading supplier of cadmium metal. We offer ultra-high purity Cd Metal (up to 99.99999%) with superior quality and competitive prices.
Related product: Cadmium Sulfide Powder, Cadmium Selenide Powder
INQUIRY
Add to Inquiry List
Description
Specification
Technical Data Sheet
Video
LATEST RECOMMENDED

VD0539 Cadmium (Cd) Evaporation Materials

VD0774 Cadmium Fluoride (CdF2) Evaporation Materials

VD0813 Cadmium Sulfide (CdS) Evaporation Materials

VD0842 Cadmium Selenide (CdSe) Evaporation Materials


SE1116 (Discontinued) Cadmium Selenide Powder (CdSe Powder) (CAS No.1306-24-7)


FL1202 (Discontinued) Cadmium Fluoride (CdF2•xH2O) Powder (CAS No. 7790-79-6)


NN1599 (Discontinued) Nano Cadmium Sulfide Powder


CD2210 (Discontinued) Cadmium Chloride Powder (CAS No. 10108-64-2)
GET A QUOTE
Send us an Inquiry now to find out more Information and the latest prices,thanks!