Rhodium: Element Properties and Uses
Description
Rhodium is a rare, silvery-white metal celebrated for its exceptional catalytic and reflective properties, essential in automotive, chemical, and industrial applications.
Introduction to the Element
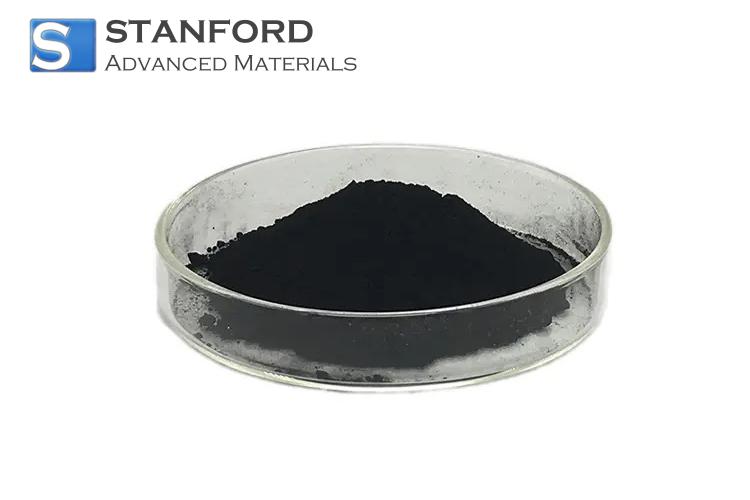
Rhodium is a transition metal that belongs to the platinum group and is recognized for its rarity and remarkable characteristics. Discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston, this element is represented by the symbol Rh and holds the atomic number 45. As one of the least abundant elements on Earth, rhodium naturally occurs in ores alongside other platinum group metals.
Chemical Properties Description
Rhodium exhibits a set of chemical properties that render it highly useful in industrial applications. Chemically inert in many environments, the element is renowned for its excellent resistance to corrosion. This characteristic is a result of a naturally forming protective oxide layer that prevents further chemical reactions. In addition, rhodium can exist in various oxidation states, although its most common and stable state is zero. Such stability under diverse conditions makes rhodium particularly suitable for use as a catalyst in reactions that require longevity and reliability.
Physical Properties
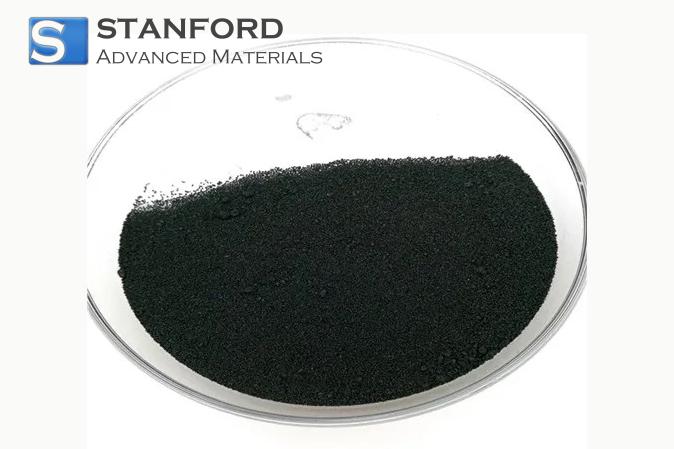
In addition to its chemical properties, rhodium is distinguished by several notable physical characteristics. The metal has a silvery-white appearance with a highly reflective surface that is prized in both decorative and functional applications. Its density is moderately high, contributing to its strength and durability in demanding environments. Rhodium's high melting and boiling points make it an ideal choice for applications that involve extreme temperatures. These physical properties ensure that rhodium maintains its structural integrity even under conditions that would compromise many other materials. For more information, please check Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM).
Preparation Methods
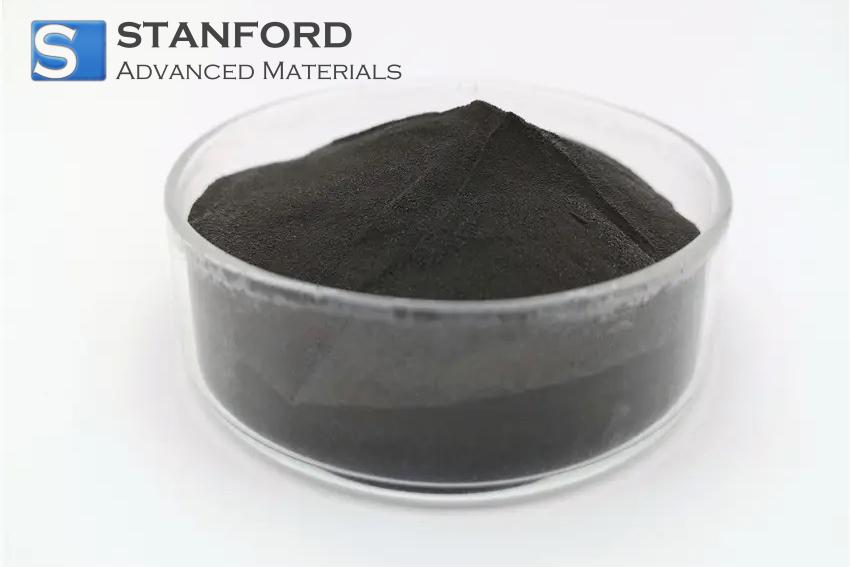
The preparation of rhodium for industrial use is a complex process, as the metal is never found in its pure form naturally. Instead, it is extracted from ores that contain several platinum group metals. The extraction process begins with the mechanical crushing and milling of the ore to increase the surface area available for chemical treatment. This is followed by a series of chemical processes, including smelting and precipitation, which separate rhodium from other metals.
Common Uses
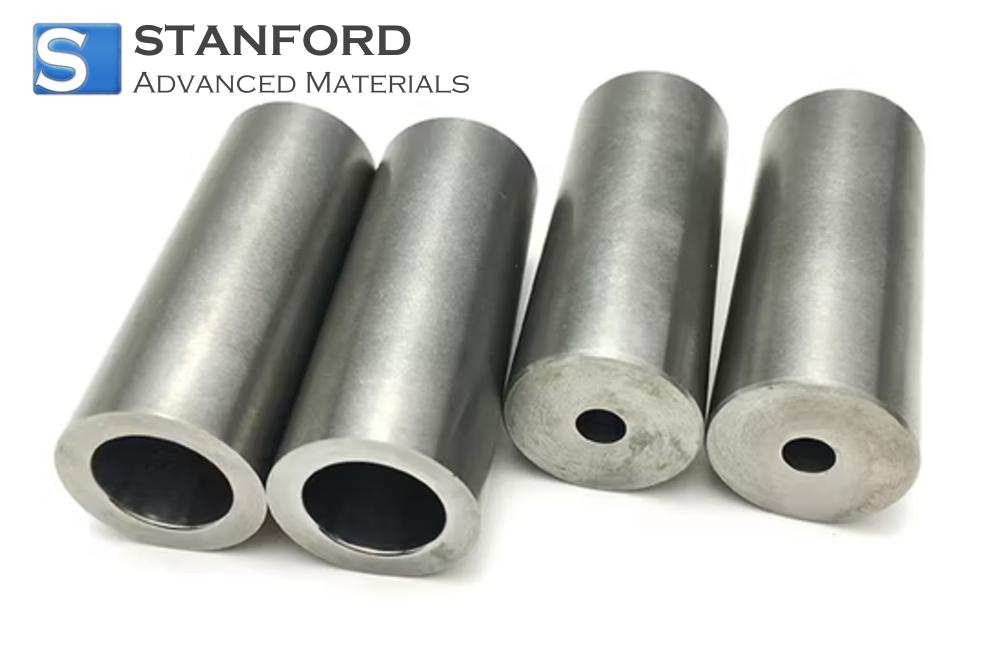
Rhodium plays a crucial role in numerous industrial products due to its unique properties. One of the most prominent applications is in the automotive industry, where rhodium is used in catalytic converters. These converters are essential in reducing harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful compounds.
In the chemical sector, rhodium serves as a catalyst in the synthesis of nitric acid and other important chemicals, contributing to efficient and reliable production processes.
The jewelry industry also benefits from rhodium; it is frequently used to plate precious metals, enhancing their shine and resistance to tarnish.
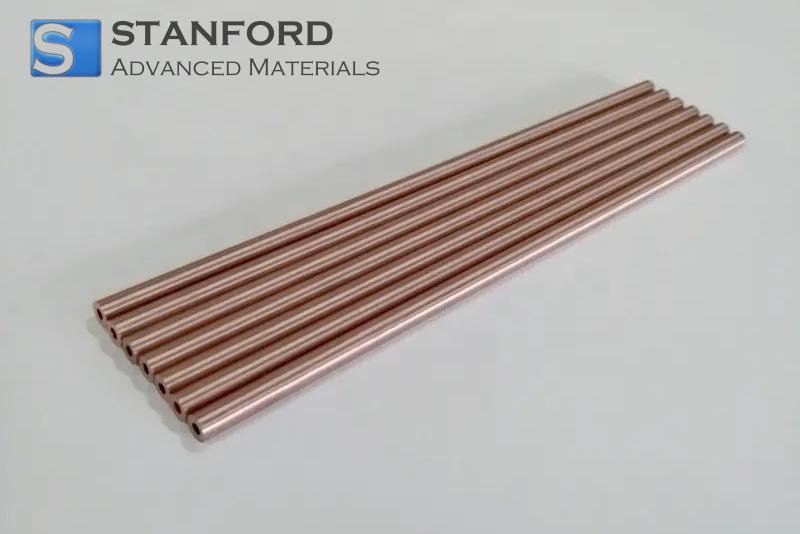
Beyond these applications, rhodium is found in a variety of high-tech industrial products such as electrical contacts, thermocouples, and reflective coatings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Rhodium?
Rhodium is a rare, silvery-white transition metal known for its exceptional
resistance to corrosion and high catalytic efficiency.
How is Rhodium extracted?
Rhodium is extracted from platinum group ores using a series of chemical
processes including smelting and ion exchange techniques.
What are the common uses of Rhodium?
Rhodium is commonly used in automotive catalytic converters, chemical
catalysts, jewelry plating, and various high-tech industrial products.
How does Rhodium compare to other precious metals?
Compared to platinum and palladium, Rhodium offers superior corrosion
resistance and reflectivity, making it highly valuable in specialized
applications.
Are there sustainable methods for producing Rhodium?
Yes, modern research focuses on improving recycling processes and sustainable
extraction methods to reduce the environmental impact of Rhodium production.