Photoelasticity: Stress Analysis through Light
Introduction
Photoelasticity is a valuable experimental method used in engineering and materials science to measure and visualize the stress distribution within transparent materials. By utilizing the phenomenon of birefringence, photoelasticity provides a non-destructive means to analyze how materials respond under various loading conditions.
Basic Principles
Birefringence
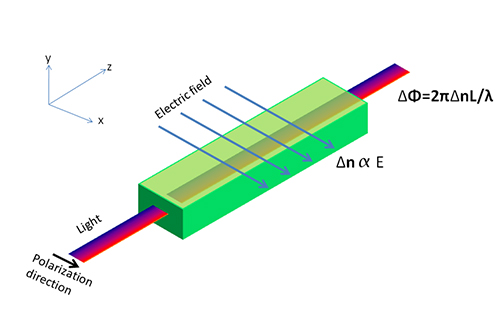
Birefringence is the optical property of a material where the refractive index depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. When a transparent material is subjected to stress, it exhibits birefringence proportional to the applied stress, allowing for the visualization of stress patterns.
Stress-Induced Birefringence
In photoelasticity, when a material is stressed, the internal strains induce birefringence. By passing polarized light through the material, the changes in polarization caused by stress can be observed as colorful patterns, known as fringes, which correlate to the stress distribution.
Measurement Techniques
Model Preparation
Accurate photoelastic analysis begins with creating a model of the structure under investigation. The model must be made from a photoelastic material, typically epoxy resins or polycarbonate, ensuring uniform optical properties.
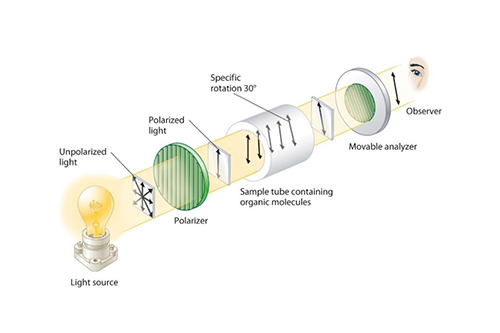
Light Source and Polarizers
A coherent light source is used in conjunction with polarizers. The first polarizer, known as the polarizer, aligns the light's polarization before it enters the stressed model. After passing through the model, a second polarizer, the analyzer, is oriented to detect changes in polarization due to birefringence.
Photoelasticity Stress Analysis
Photoelastic stress analysis involves interpreting the fringe patterns obtained from photoelastic experiments. Each fringe corresponds to a specific stress level, allowing engineers to quantify and assess the integrity of materials and structures under load.
Applications
Photoelasticity is widely used in various fields, including mechanical engineering, aerospace, civil engineering, and materials science, to assess components such as beams, shafts, and complex assemblies under operational stresses.
|
Aspect |
Description |
|
Measurement Technique |
Uses polarized light to detect stress-induced birefringence |
|
Basic Principles |
Relies on the change in refractive index under stress |
|
Key Phenomena |
Birefringence and fringe pattern formation |
|
Stress Analysis |
Quantifies stress distribution within materials |
|
Applications |
Structural analysis, material testing, design validation |
For more information, please check Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM).
Frequently Asked Questions
What is photoelasticity used for?
Photoelasticity is used to measure and visualize stress distribution in materials, aiding in structural analysis and design optimization.
How does birefringence relate to stress?
Birefringence in materials increases proportionally with the applied stress, allowing stress patterns to be visualized using polarized light.
What materials are suitable for photoelastic analysis?
Transparent materials like epoxy resins and polycarbonate are commonly used due to their uniform optical properties.
Can photoelasticity provide quantitative data?
Yes, with proper calibration, photoelasticity can offer quantitative measurements of stress magnitudes through fringe analysis.
What equipment is needed for photoelastic stress analysis?
A polarized light source, photoelastic model, polarizers, and a camera or sensor to capture fringe patterns are essential for photoelastic stress analysis.