- Products
- Categories
- Blog
- Podcast
- Application
- Document
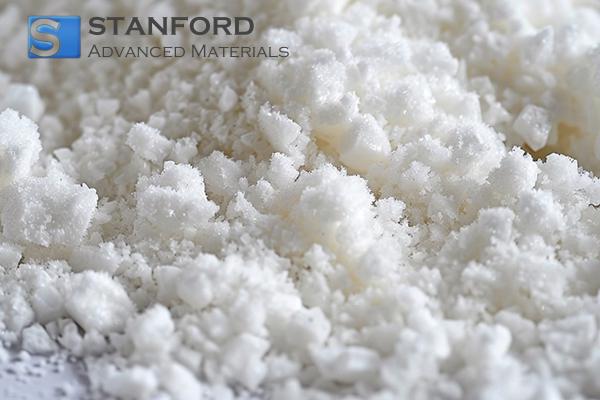
GA1145 Gallium (III) Nitrate Hydrate (Ga(NO3)3) Powder (CAS No.69365-72-6)
| Catalog No. | GA1145 |
| Purity | ≥99.99% |
| CAS Number | 69365-72-6 |
| Appearance | Crystal |
| Molecular Formula | Ga(NO3)3 · xH2O |
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a leading supplier of Gallium (III) Nitrate Hydrate. We use our experience and expertise to provide the highest quality products and the shortest delivery time.
Related products: Gallium Metal, Gallium Arsenide, Gallium Nitride, Gallium (III) Selenide, Gallium (III) Sulfide, Gallium Oxide
INQUIRY
Add to Inquiry List
Description
Specification
Technical Data Sheet
LATEST RECOMMENDED

VD0621 Copper Gallium (Cu/Ga) Evaporation Materials

VD0690 Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide (InGaZnOx) Evaporation Materials

VD0744 Zinc Oxide doped with Gallium Oxide (ZnO/Ga2O3) Evaporation Materials

VD0843 Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS) Evaporation Materials

VD0846 Gallium Selenide (Ga2Se3) Evaporation Materials

VD0860 Gallium Telluride (Ga2Te3) Evaporation Materials

SE2799 Gallium (II) Selenide (GaSe) Powder (CAS 12024-11-2)


GA1142 (Discontinued) Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) (CAS No.1303-00-0)
GET A QUOTE
Send us an Inquiry now to find out more Information and the latest prices,thanks!